

 Fuel Cell
Fuel Cell

 Fuel Cell
Fuel Cell home > Research > Research Area > Fuel Cell
home > Research > Research Area > Fuel Cell
-
연구주제 (Research Areas)
◆ Power Conversion Circuit Design and Control Algorithm for Electric Vehicles (EV) and Fuel Cell EV
◆ Power Conversion Applications : Electric Machine Drives (DC/BLDC/PMSM/IM) based on Microprocessors,
Design and Control of Power Converters (DC to DC, AC to DC, DC to AC, AC to AC)
◆ Power Electronics Circuits and Control, Interface for Distributed Generation Systems Using Renewable Energy Sources (Wind Turbines/Photovoltaic Arrays/Fuel Cells/Energy Storage Devices)
◆ Driving Circuits and Driving Methods of AC Plasma Display Panel (PDP) and Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
연료전지는 '전지'라는 말이 붙어있기는 하지만 일반적인 전지와는 다르다. 전지는 닫힌 계에 화학적으로 전기에너지를 저장하는 반면, 연료전지는 연료를 소모하여 전력을 생산한다. 또한 전지의 전극은 반응을 하여 충전/방전 상태에 따라 바뀌지만, 연료전지의 전극은 촉매작용을 하므로 상대적으로 안정하다.
연료와 산화제로는 여러 가지를 이용할 수 있다. 수소 연료전지는 수소를 연료로, 산소를 산화제로 이용하며, 그 외에 탄화수소, 알코올 등을 연료로, 공기, 염소, 이산화 염소 등을 산화제로 이용할 수 있다.
연료전지의 발전 효율은 40~60% 정도로 대단히 높으며, 반응 과정에서 나오는 배출열을 이용하면 전체 연료의 최대 80%까지 에너지로 바꿀 수 있다. 게다가 천연 가스와 메탄올, LPG(액화석유가스, propane gas), 나프타, 등유, 가스화된 석탄 등의 다양한 연료를 사용할 수 있기 때문에 에너지자원을 확보하기 쉽다. 또한 연료를 태우지 않기 때문에 지구 환경보호에도 기여할 수 있다. 또한 질소산화물(NOx)과 이산화탄소의 배출량이 석탄 화력 발전의 각각 1/38과 1/3 정도이며, 소음도 화력발전 방식에 비해 매우 적다는 장점이 있다. 이와 더불어 모듈화에 의한 건설 기간의 단축, 설비 용량의 증감이 가능하고, 화력발전 방식에 비해 훨씬 적은 토지 면적을 필요로 하기 때문에 입지 선정이 용이하다. 따라서 도심 지역 또는 건물 내에 설치하는 것이 가능하여 경제적으로 에너지를 공급할 수 있다. 연료전지는 기존의 화력 발전을 대체할 수 있으며, 분산 전원용 발전소, 열병합 발전소, 더 나아가서는 무공해 자동차의 전원 등에 적용될 수 있다.
< 출처 : http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EC%97%B0%EB%A3%8C%EC%A0%84%EC%A7%80 >
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through an electrochemical reaction of hydrogen fuel with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Fuel cells are different from batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy comes from chemicals already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied.
The first fuel cells were invented in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came more than a century later in NASA space programs to generate power for satellites and space capsules. Since then, fuel cells have been used in many other applications. Fuel cells are used for primary and backup power for commercial, industrial and residential buildings and in remote or inaccessible areas. They are also used to power fuel cell vehicles, including forklifts, automobiles, buses, boats, motorcycles and submarines.
There are many types of fuel cells, but they all consist of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte that allows positively charged hydrogen ions (protons) to move between the two sides of the fuel cell. At the anode a catalyst causes the fuel to undergo oxidation reactions that generate protons (positively charged hydrogen ions) and electrons. The protons flow from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte after the reaction. At the same time, electrons are drawn from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit, producing direct current electricity. At the cathode, another catalyst causes hydrogen ions, electrons, and oxygen to react, forming water. Fuel cells are classified by the type of electrolyte they use and by the difference in startup time ranging from 1 second for proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEM fuel cells, or PEMFC) to 10 minutes for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC). A related technology is flow batteries, in which the fuel can be regenerated by recharging. Individual fuel cells produce relatively small electrical potentials, about 0.7 volts, so cells are "stacked", or placed in series, to create sufficient voltage to meet an application's requirements. In addition to electricity, fuel cells produce water, heat and, depending on the fuel source, very small amounts of nitrogen dioxide and other emissions. The energy efficiency of a fuel cell is generally between 4060%; however, if waste heat is captured in a cogeneration scheme, efficiencies up to 85% can be obtained.
< Source : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fuel_cell >
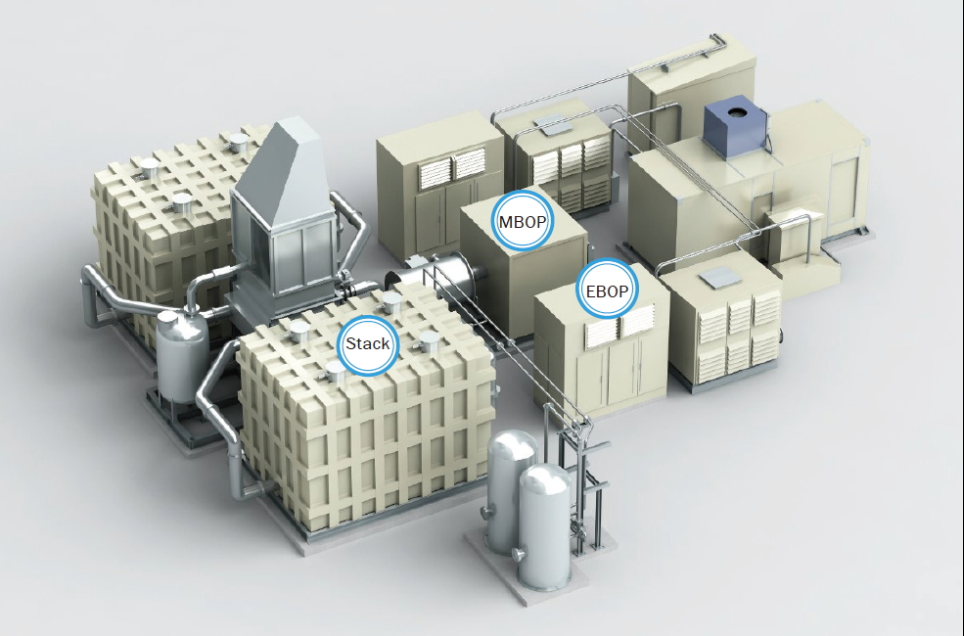
< Source : http://kospomagazine.co.kr>


